The yellow dwarf star that fuels our sun is a hot torch of hydrogen and helium plasma that bears twins and, briefly, flares up.This fusion of hydrogen nuclei calls for a crystal clear and progressive shift of embryonic states. It is a model of 5 billion years old and is at the dead end of our planetary system. It is the only luminous body of the solar family, approx. 150 million km (93 million miles) from our planet. This is how a planet without the energy (photosynthesis) from the sun could not give rise to life as we know it.
The sun may look like just a stable source of heat and light on this earth that we are permanently staring at. Nevertheless, the Sun is a varying star that gives up energy on a regular basis. Heliophysics is the science of the sun and the solar system, in which the sun provides a leading effect on the solar system. The top of our solar system is our sun. It is nearly 1 for diameter, 4 million kilometers, or 865,000 miles. The gravitational attraction of the solar system works so effectively for not only the largest planets but also the tiniest junk particles.
The Sun, being a medium-sized star, is only the second-largest of millions of other stars. It is not the hub of our solar system, and without it, human life would almost have no existence. Among the stars, there are also ones that are sixty times more massive than the sun. Also, beside one star, there are a lot of systems comprised of multiple stars. Scientists can get an idea of how distant the universe the universe starts by examining our sun.
At the very center of the sun, which can be as high in temperature as 27 million degrees F (15 million degrees C), lies its hottest region. The photosphere (the portion of the sun that we refer to as its surface) is warm in comparison to the outer solar layers. Its slightly cooler temperature is about 10,000 °F (5,500 ºC). The sun’s crown, or corona, gets extraordinarily hotter as it comes longer away from the surface; therefore, it can be the answer to the sun’s greatest mystery. If, for example, you think the corona is sizzling hotter than the photosphere, then you are in for a big surprise. The corona can reach up to three times the photosphere’s temperature, according to NASA. 5 million © F (2 million °C).
Interesting facts about Sun –
Potential for Life:
The sun is too powerful to host environments similar to the ones on our planet with radiant temperatures and harmful solar rays. While it is the sun and its light that make the earth habitable, it is only due to the sun and its activity that life is possible on the earth.
Moons:
The planets, along with the moons, revolve around the sun. However, the sun is not where moons exist, as it is a star.
Namesake:
It is variously called the Great Bear, the Raven, the Seagull, or the Moon. Because of the primary adjective “solar,” both Sun and the Latin word for sun come from the same language.After that, by knowing the name of a Greek god of the sun, “Helios,” the sky-high heliosphere and helioseismology can be easily reordered.
Ring:
The solar system today is the result of its birth some 4.6 billion years ago, when the Sun would have been orbited by a dusty and gas-filled disk. Among the clouds of dust that are connected to our sun, some of that dust is accumulating to this day. They determine trajectories, picturing the movements of planets, whose gravitational influence shapes up the adjustments that lie beneath the Sun’s fixed paths.
Rotation and Orbit:
The Milky Way galaxy consists of the Orion Spur, a spiral branch, from which the Sagittarius arm is diverged, with the Sun being part of this arm. Together with planets, asteroids, comets, and other solar system elements, our sun orbits the center of the Milky Way too. As per normal standards, the mean speed of our solar system is 450,000 miles per hour (720,000 kilometers per hour). Nevertheless, this high speed could make processes such as the sun’s complete orbit around the Milky Way take up to 230 million years to complete.
In its procession around the galaxy, the sun spins around itself. Its spin is 7. As a result, it varies between 19.5 degrees and 25 degrees with regard to the orbital plane of the planets. We cannot think of the sun as a solid; therefore, its core is the hottest part, and then its outermost region, comprising the photosphere, rotates differently. The rotation of the sun relative to the earth is about 36 hours near the poles; that is, 25 hours at the equator.
Surface :
Nevertheless, the sun is different from Earth and other rocky planets and moons as it is made up mainly of gases without a solid surface. The photosphere is the part of the sun that is constantly in the news and recognized as the solar surface. Because it is the layer that emits the most visible light, the word “photosphere” was coined to describe this part of the sun. “It is the fragment of the moon on display from the Earth, or simply the manmade piece on show for people here on Earth.” (I really hope this is obvious, but always shield your eyes when you do stare at it.)
Atmosphere:
The photosphere includes the corona, the transition zone, and the chromosphere area situated above it. The important point is that there is a ‘transition’ layer as depicted in the illustration where the chromosphere rapidly changes temperatures and then becomes the corona; some scientists, however, do not identify this layer as a separate region. The sun’s atmosphere is built by the photosphere, chromosphere, and corona. (It is also known as the sun´s outer layer, which deadpan humorists refer to as “the sun´s atmosphere.”)) Such characteristics as solar flares, coronal holes, and sunspots come from the sun’s atmosphere.

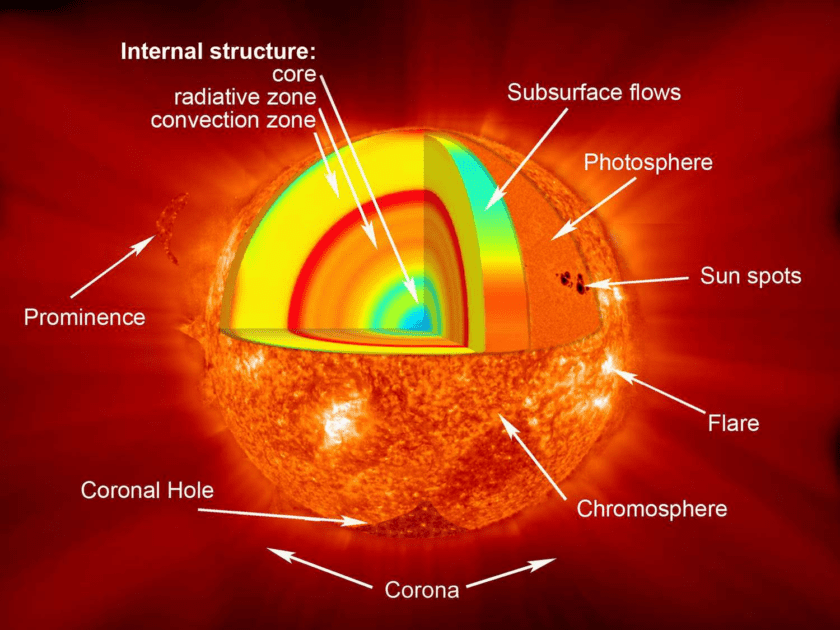
Structure:
The sun is an immense sphere composed of helium and hydrogen, which are held together by gravitational force. The sun possesses different regions. These internal regions consist of a convection zone, a radiative zone, and a core zone. Next in order is the photosphere, which is the visible surface, then the chromosphere, the transition zone, and finally the corona, which is the enormous outer atmosphere, the outermost layer. The solar wind, in the form of coronal plasma that moves supersonically, constitutes the big magnetic “bubble” named the heliosphere, which encompasses the Sun. In the solar system, the heliosphere extends even beyond the orbit of the last planet. Earth, therefore, belongs to the sun’s outer gas layer. Interstellar space is the region that appears beyond the atmosphere.
The sun’s hottest spot is its inner core. The sun’s heat and light originate from the process of fusing hydrogen into helium in the core of the sun. It is extremely high-temperature—27 million °F (15 million °C)—and has a thickness of 86,000 miles (138,000 km). The solar core has a density of 150 g/cm2. The density of titanium is approximately 2.5 times that of lead. It weighs more than 8.3 times the density of lead and almost 13 times the density of gold.
Radiation, on the other hand, is the process whereby energy radiates outward from the core. In fact, this radiation takes around 170 thousand years to get from the core to the top of the convection zone, as it merely goes around the radiative zone. Outside the range, the temperature becomes some point less than 3. And in the convection zone, the temperature reaches 5 million °F (2 million °C). Large pockets of hot plasma, or the ocean of ionized particles, are depicted in this image as rising in the photosphere that constitutes the sun’s surface, usually.
Formation:
The sun was formed in the solar nebula, which is a huge rotating cloud made of gas and dust.More than 4 billion years ago. 6 billion years ago. The nebula started to rotate more and elongated into a disk as a result of its own gravity collapse. The entire nebular substance went to the center to form our sun, and as a result, it made up only 1% of its mass. 8% of the total mass of the solar system. The planets and other objects that today circle around the sun are the result of a substantial part of the debris from the collisions. (The solar wind from the young sun affected it so that it cleared the last gas and dust away.)
The same thing would happen to our sun, just as all the other stars face. As it dies, the sun will grow bigger and bigger, and it will finally be a red giant star, big enough to gobble Venus, Mercury, and maybe even the Earth. Based on scientific predictions, the sun is right now in the middle of its life cycle and will be shining for another 5 billion years and more before it becomes a white dwarf.
Size and Distance
For example, our Sun, a middle-sized star, has a radius of about 435,000 miles (700,000 kilometers). While many stars are far larger than our planet, the Sun is far more massive than it is, not the least of which is that more than 300,000 Earth likes in mass are needed to equal the Sun, just as an example. For this piece to be full, we would need 3 million planets the size of Earth. There are more than 150 million kilometers, or 93 million miles, that lie between us and the sun. Our nearest star after the sun is the Alpha Centauri star, which is composed of two sun-like stars, Alpha Centauri A and B, and one red dwarf star, Proxima Centauri. It is about 4.24 light-years away. Light can travel the distance in one year that is called a light-year, which is approximately 6 trillion miles.

