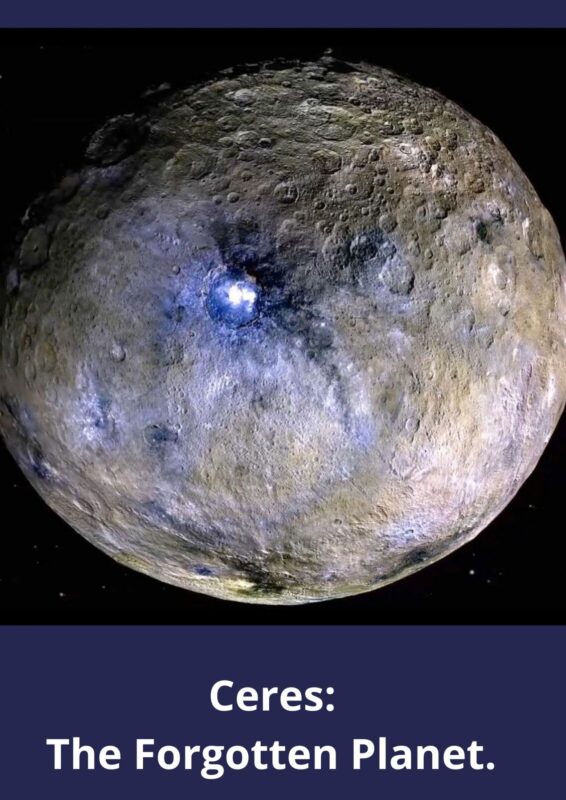
Did you know Ceres is one of the only dwarf planets that is found in the asteroid belt in the inner solar system? Did you know the number of times the status of Ceres was changed? You wouldn’t believe it, seriously! Let us look into the journey of Ceres – from its discovery to its present status and everything in between.
First, we will get familiar with a few terms.
- Asteroid – Airless, rocky remnants left over from the early formation of our solar system that revolve around the Sun and are too small to be called planets.
- Comet – Icy bodies in space that release gas or dust and orbit around the Sun.
- Planet – a celestial object that:
- Orbits the Sun.
- Has enough mass to be round, or nearly round.
- It has removed debris and small objects from the area around its orbit.
- Dwarf Planet – a celestial object that orbits the Sun, has sufficient mass to be round but doesn’t have enough gravity to be able to remove the debris in its orbit. The last criterion is the only point at which planets and dwarf planets differ!
Introduction
History and discovery
In the search of a star, Giuseppe Piazzi, the Italian astronomer stumbled in 1801 upon a bright object he believed to be a comet. Later, with the help of another astronomer, it was concluded that the object discovered was a planet. Giuseppe named it Ceres, after the Roman goddess of agriculture, grain, and motherly love.
As more objects were discovered in the same region along with smaller bodies scattered in the asteroid belt, Ceres was demoted to the status of the asteroid. In 2006, Ceres was finally promoted to the status of a dwarf planet though it often retains its classification as an asteroid as well. Ceres is the only dwarf planet in the Solar System and is the largest asteroid in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Unlike other rocky bodies in the asteroid belt, Ceres is an oblate spheroid, rounded with a rotational bulge around its equator.
Distance and Size
As Ceres is the largest asteroid present in its belt, it encompasses one-third of all the mass found in the asteroid belt. Located just under 2.8 Astronomical Units away from the Sun, it receives light in about 22 minutes (Earth receives sunlight in 8.3 minutes!). From Earth, Ceres is approximately 3.5 Astronomical Units away and with a radius of 296 miles (476 kilometers), it is 1/13 the radius of Earth. Imagine Earth the size of a nickel, compared to it, Ceres would be as big as a poppy seed!

Formation and Structure
Ceres, also called by Scientists as “embryonic planet” or “protoplanet”, meaning that it started to form as a planet but failed to finish, is believed to have been formed around 4.5 billion years ago when the solar system was forming. Gravity did its work by pulling swirling gas and dust and resulted in the creation of the dwarf planet!
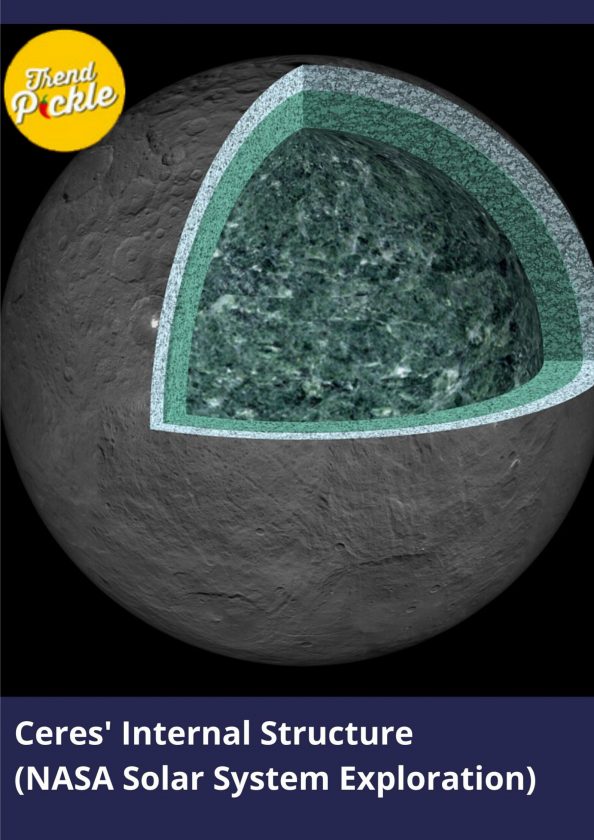
Ceres is similar to the terrestrial planets (Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars) in a way that it also has a layered interior though its layers aren’t as clearly defined. Ceres has a solid core and a mantle made of water ice. In fact, it has more water than Earth! And yes, Scientists are already looking for the possibility of life there.
Ceres’ crust is rocky and dusty with large salt deposits. The salt found on its crust isn’t like our table salt i.e., Sodium Chloride but instead made of different minerals like Magnesium Sulphate.
Orbit and Rotation
It follows an orbit around Mars and Jupiter, within the asteroid belt and closer to the orbit of Mars. It takes about 4.6 Earth years or 1,682 Earth days for Ceres to make one trip around the sun. Ceres’ day length is one of the shortest in the solar system as it completes one rotation every 9 hours. Due to only a 4-degree tilt of its axis of rotation with respect to the plane of its orbit around the sun, it doesn’t experience seasons like other more tilted planets do.

Atmosphere
Ceres has a very thin atmosphere, and there is evidence it contains water vapor. This water vapor is believed to be a result of either ice volcanoes or sublimation of ice near its surface.
Is life possible on Ceres?
After learning about the presence of such an amount of water, one could say there is a slight if not more a possibility of life there. Scientists were curious to find more about Ceres after discovering water.
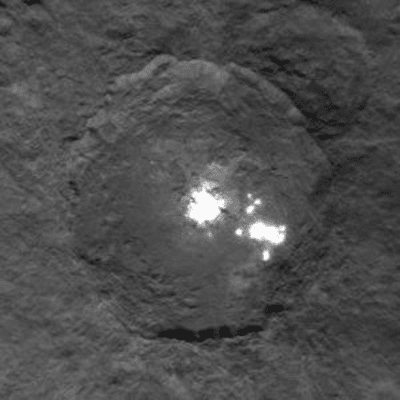

Bright spots on Ceres.
And in 2015, when Dawn spacecraft (launched by NASA for the purpose of studying Ceres and Vesta) detected bright spots on Ceres’ surface, it made scientists all over the world argue about the possible reasons and theories that resulted in these spots. Mostly it was believed that these bright spots composed of sodium carbonate salts. However, there is no tough proof of whether Ceres could habitat life or not.

