Coronaviruses are a group of viruses that cause diseases in mammals and birds. In humans, the viruses cause respiratory infections which are typically mild, including the common cold; however, rarer forms such as SARS, MERS and the novel coronavirus causing the current outbreak can be lethal. In cows and pigs, they may cause diarrhea, while in chickens they can cause an upper respiratory disease. There are no vaccines or antiviral drugs that are approved for prevention or treatment.
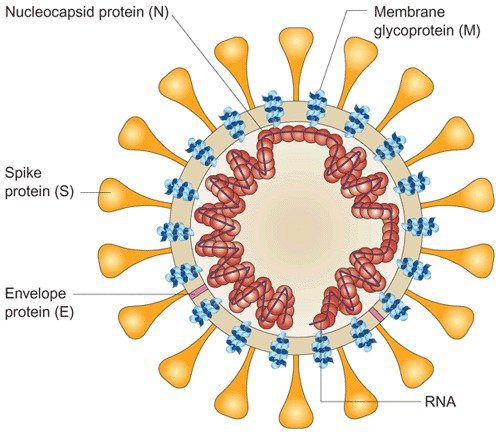
Coronaviruses are viruses in the subfamily Ortho corona virinae in the family Coronaviridae, in the order Nidovirales. Coronaviruses are enveloped viruses with a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome and with a nucleocapsid of helical symmetry. The genomic size of coronaviruses ranges from approximately 26 to 32 kilobases, the largest for an RNA virus.
The name “coronavirus” is derived from the Latin corona, meaning crown or halo, which refers to the characteristic appearance of the virus particles (virions): they have a fringe reminiscent of a royal crown or of the solar corona.
Diseases caused
Coronaviruses primarily infect the upper respiratory and gastrointestinal tract of mammals and birds. They also cause a range of diseases in farm animals and domesticated pets, some of which can be serious and are a threat to the farming industry. In chickens, the infectious bronchitis virus (IBV), a coronavirus, targets not only the respiratory tract but also the urogenital tract. The virus can spread to different organs throughout the chicken.
Economically significant coronaviruses of farm animals include porcine coronavirus (transmissible gastroenteritis coronavirus, TGE) and bovine coronavirus, which both result in diarrhea in young animals. Feline coronavirus: two forms, feline enteric coronavirus is a pathogen of minor clinical significance, but spontaneous mutation of this virus can result in feline infectious peritonitis (FIP), a disease associated with high mortality.
Similarly, there are two types of coronavirus that infect ferrets: ferret enteric coronavirus causes a gastrointestinal syndrome known as epizootic catarrhal enteritis (ECE) and a more lethal systemic version of the virus (like FIP in cats) known in ferrets as ferret systemic coronavirus (FSC).
Types
There are two types of canine coronavirus (CCoV), one that causes mild gastrointestinal disease and one that has been found to cause respiratory disease. Mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) is a coronavirus that causes an epidemic murine illness with high mortality, especially among colonies of laboratory mice. Sialodacryoadenitis virus (SDAV) is a highly infectious coronavirus of laboratory rats, which can be transmitted between individuals by direct contact and indirectly by aerosol. Acute infections have high morbidity and tropism for the salivary, lachrymal and harderian glands.
An HKU2-related bat coronavirus called swine acute diarrhea syndrome coronavirus (SADS-CoV) causes diarrhea in pigs.
Prior to the discovery of SARS-CoV, MHV had been the best-studied coronavirus both in vivo and in vitro as well as at the molecular level. Some strains of MHV cause progressive demyelinating encephalitis in mice which has been used as a murine model for multiple sclerosis. Significant research efforts have been focused on elucidating the viral pathogenesis of these animal coronaviruses, especially by virologists interested in veterinary and zoonotic diseases.
Advice for public
- Frequently clean hands by using alcohol-based hand rub or soap and water;
- When coughing and sneezing cover mouth and nose with flexed elbow or tissue – throw the tissue away immediately and wash hands;
- Avoid close contact with anyone who has a fever and cough;
- If you have a fever, cough and difficulty breathing seek medical care early and share previous travel history with your health care provider;
- When visiting live markets in areas currently experiencing cases of a novel coronavirus, avoid direct unprotected contact with live animals and surfaces in contact with animals;
- The consumption of raw or undercooked animal products should be avoided. Raw meat, milk or animal organs should be handled with care, to avoid cross-contamination with uncooked foods, as per good food safety practices.

