Indian constitution is the set of laws which binds every Indian citizen. It provides the basic fundamental rights to every citizen of India. Constituent-makers worked very hard for three years to prepare the Indian constitution. And finally, it came into force on 26th January 1950. On the same day, Indians celebrate Republic day every year. Do you want to know more about the Indian Constitution? Here are some interesting facts about the Indian Constitution you probably didn’t know.
1. Prem Behari Narain Raizada, a calligraphist wrote the original constitution of India by hand in beautiful calligraphy. It was not typed or printed. On request of Jawaharlal Nehru, it was handwritten by Prem Behari in a flowing italic style. Many artists from Shanti Niketan including Beohar Rammanohar Sinha and Nandalal Bose decorated the pages of the constitution with various arts and paintings. The original constitution was published in Dehradun.
2. Written in Hindi and English, The original copies of the Indian Constitution are preserved in special helium-filled containers in the Library of the Parliament of India.
3. When it came into force on 26 January 1950, The constitution had 22 parts containing 395 articles and 8 schedules. As of Nov 2018, Indian constitution has 25 parts containing 449 articles ( a preamble and 448 articles), 12 schedules and 5 appendices.
4. At about 145,000 words, Indian constitution is the second-largest active constitution in the world after the Constitution of Alabama.
5. Since its enactment, The Parliament of India has amended the Indian constitution 101 times. The first amendment happened during the tenure of Prime minister Jawaharlal Nehru which became effective from 10th May 1951. During the tenure of Prime minister Narendra Modi, the latest amendment happened which introduced Good and Sevices Tax (GST) effective from 1st July 2017.
6. The 389-member Constituent assembly (reduced to 299 after the partition of India) first met on 9 December 1946 in the constitution hall, New Delhi. It took them exactly 2 years, 11 months and 18 days to prepare the final draft of the Constitution. The Constituent Assembly had eleven sessions running over a period of 165 days to come up with the final draft at a total expenditure of ₹6.4 million.
7. The Constituent Assembly appointed a total of 22 committees to handle different tasks of constitution-making. On 29 August 1947, drafting committee appointed B.R.Ambedkar as the chairman who is often credited as the chief architect of the Indian constitution.
8. On 13 December 1946, Jawaharlal Nehru moved An ‘Objective Resolution’ in the assembly, laying down the underlying principles of the constitution. It finally became the Preamble of the constitution.
9. Before the final draft was finalized, the Constituent assembly discussed the draft and made over 2000 amendments. On 26 November 1949, the Constituent Assembly adopted the constitution which was signed by 284 members. Every year, We celebrate 26th November as National Law Day or Constitution Day because this is the day when Constitution passed and accepted by the assembly.
10. The Constituent assembly’s final session was held on 24 January 1950 and it was disbanded thereafter. 284 members of the Assembly (which included 15 women) signed two handwritten copies of the constitution, one in Hindi and the other in English. It was raining outside the Parliament on that day. The members of the assembly thought of it as a good omen. Two days later, the constitution was legally enforced on 26th January 1950. Every year, We celebrate 26 January as the Republic day marking the legal enforcement of the constitution.
11. The Constitution of India is the longest written constitution of any sovereign country in the world containing 449 articles in 25 parts, with 146,385 words in its English copy. On the other side, the Constitution of Monaco is the shortest written constitution of any sovereign country in the world, containing 10 chapters with 97 articles, and a total of 3,814 words.
12. While drafting the constitution for India, assembly members took the inspiration from the constitution of other countries. Various laws and features were directly imported into our Constitution from other countries.
13. The concept of Five-Year Plans (Panch Varshiya Yojna) was taken from the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR), and the Directive Principles (socio-economic rights) were taken from Ireland constitution. The Law defining the functionality of the Supreme Court was taken from Japan.
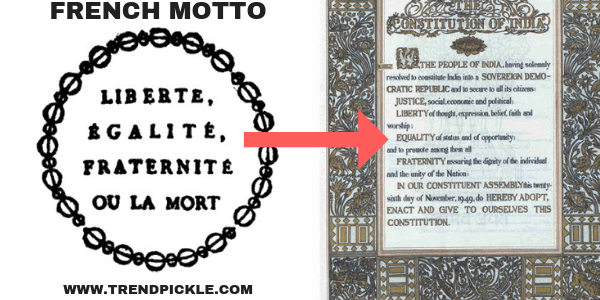
14. The concepts of Liberty, Equality, and Fraternity which appears in the preamble to Indian constitution are taken from the French constitution. These concepts are the motto of the French Republic.
15. The Preamble to the Constitution of the United States of America inspired the preamble of our Constitution, which also starts with “We the people”.
16. on 26 January 1950, The Government of India adopted the national emblem of India (the adapted version of Lion Capital of Sarnath).
17. “Abide with Me”, a Christian hymn by Scottish Anglican Henry Francis Lyte is played during Republic day celebrations as it was one of the Mahatma Gandhi’s favorite song.
18. Republic day celebrations last for three days with the “Beating the Retreat” ceremony on 29th January marking the end of celebrations.
I am sure these facts would have increased your knowledge about Indian Constitution about. If you know any other Indian constitution Facts, please let us know in the comments section.








1 comment
You put forward some strawman statements.