A vegan diet is a diet containing only plants – such as vegetables, grains, nuts and fruits – and foods made from plants. Vegans don’t eat foods that come from animals, including dairy products and eggs. One should be able to get most of the nutrients one needs from eating a varied and balanced vegan diet. One must eat at least five portions of a variety of fruit and vegetables every day. Here are the meals and health benefits of vegan diet.
A healthy vegan diet includes:
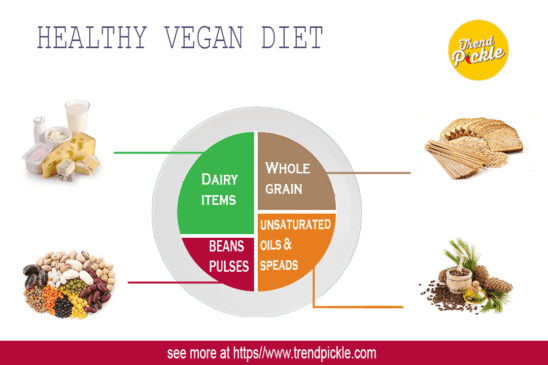
– Base meals on potatoes, bread, rice, pasta or other starchy carbohydrates. Choose wholegrain where possible.
– Some dairy alternatives (such as soya drinks and yoghurts). Choose lower-fat and lower-sugar options. –
– Some beans, pulses and other proteins.
– Unsaturated oils and spreads (eat in small amounts).
– Drink plenty of fluids – it is recommended to have 6-8 cups/glasses a day.
Supplements you need in a Vegan Diet –
A good meal planning is required for a healthy, balanced vegan diet so that you can get all the nutrients that your body needs. It is necessary to plan your meal otherwise there is a possibility that you could miss out on essential nutrients, such as calcium, iron and vitamin B12.
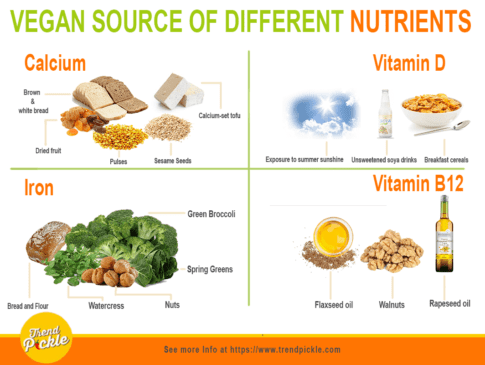
Vegan source of different nutrients –
The following are the sources of a few nutrients-
Vegan sources of calcium –
Calcium is needed for strong and healthy bones and teeth. Non-vegans get most of their calcium from dairy foods (milk, cheese and yogurt), but vegans can get it from other foods like:
– Fortified, unsweetened soya, rice, and oat drinks
– Calcium-set tofu
– Sesame seeds
– Pulses
– Brown and white bread (in the UK, calcium is added to white and brown flour by law)
– Dried fruit, such as raisins, prunes, figs, and dried apricots.
Vegan sources of Vitamin D –
The body needs vitamin D to regulate the amount of calcium and phosphate in the body. These nutrients help keep bones, teeth, and muscles healthy. Vegan sources of vitamin D are:
– Exposure to summer sunshine
– Fortified fat spreads, breakfast cereals and unsweetened soya drinks (with vitamin D added)
– Vitamin D supplements include
Vegan sources of iron –

Iron is essential for the production of RBCs (red blood cells). Good sources of iron for are:
– Pulses
– Wholemeal bread and flour
– Breakfast cereals added with iron
– Dark-green leafy vegetables, such as watercress, broccoli, and spring greens
– Nuts
– Ddried fruits such as apricots, prunes, and figs
Vegan sources of Vitamin B12 –
The body needs vitamin B12 to maintain healthy blood and a healthy nervous system. Sources of vitamin B12 for vegans include:
– Breakfast cereals added with B12
– Unsweetened soya drinks fortified with vitamin B12
– Yeast extract such as Marmite, which is fortified with vitamin B12
Vegan sources of omega-3 fatty acids –
Omega-3 fatty acids, primarily those found in oily fish helps to maintain a healthy heart and reduce the risk of heart disease when eaten as part of a healthy diet. Sources of omega-3 fatty acids suitable for vegans include:
– Flaxseed (linseed) oil
– Rapeseed oil
– Soya oil and soya-based foods, such as tofu
– Walnuts
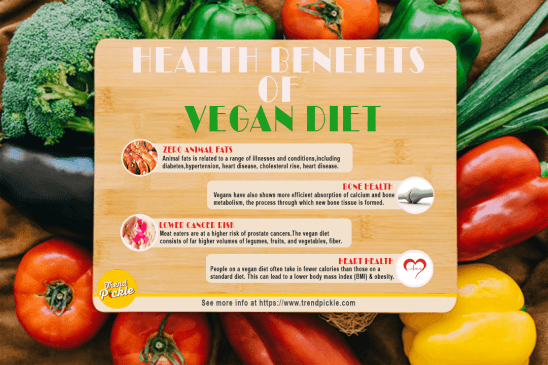
Health Benefits of Vegan Diet –
The Health benefits of vegan diet are as follows –
Zero animal fats –
Animal fats is related to a range of illnesses and conditions, including diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, hypertension, heart disease, cholesterol rise, and various cancers. By cutting these from the diet, the risk of many health issues can be greatly reduced.
Lower cancer risk –
Meat eaters are at a higher risk of colorectal and prostate cancers. The vegan diet consists of far higher volumes of legumes, fruits, and vegetables, fiber, and vitamin C. These are believed to protect against a variety of cancers.
Bone health –
A vegan diet has shown benefits for the generation of new bone tissue. Calcium is important for bone and dental health. Milk and cheese are good sources of calcium for a normal person but for vegan figs, kale, spinach, black-eyed peas, and turnip greens can be excellent sources of calcium. Vegan milk alternatives are becoming widely available such as soy milk, almond milk, and even vegan cheese.
Bones also need vitamins D and K, potassium, and magnesium. Soy, fruit and some vegetables contain appropriate amounts of these nutrients without the health risks of animal fats. Daily exposure to the sun also enables the body to make vitamin D.
Vegans have also shown more efficient absorption of calcium and bone metabolism, the process through which new bone tissue is formed.
Heart health –
People on a vegan diet often take in fewer calories than those on a standard diet. This can lead to a lower body mass index (BMI) and a reduced risk of obesity.
Lower levels of harmful cholesterol mean that vegans have a lower risk of mortality from stroke and ischemic heart disease than people who eat meat.
Protecting against chronic disease –
Plant-based diets can forestall an individual’s genetic likelihood of developing a chronic disease, such as type 2 diabetes. A 2008 study explains that bioactive compounds in plant foods can control biological factors that may work against the genetic factors linked to some chronic diseases. The researcher’s further state that the antioxidants in plant-based foods can combat free radical cells that cause cell damage and inflammation.
Other plant compounds can help to control different genes linked to cardiovascular disease, arterial plaque, and tumor growth.
Which is your favourite vegan meal, let us know in the comment section.

