Mohenjo-Daro is an archaeological site in the province of Sindh, Pakistan. The words ‘Mohenjo Daro’ literally translate to ‘the mound of the dead’. The city of Harappa and other important Indus Valley sites were found on a series of the rounded pile, hence known as Mohenjo-Daro. Built around 2500 BCE, it was one of the largest settlements of the ancient Indus Valley civilization, and one of the world’s earliest major cities, contemporary with the civilizations of ancient Egypt, Mesopotamia, Minoan Crete, and Norte Chico. As of now, it is about 5000 years old civilization. Mohenjo-Daro was abandoned in the 19th century BCE as the Indus Valley Civilization declined, and it was discovered in 1920. Significant excavation has since been conducted at the site of the city. It also has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1980. Let’s look at some unknown facts about Mohenjo Daro civilization.
1. It is the best-preserved city of Indus Valley civilization. It was built around 2500 BC. It is approximately the same time when pyramids of Egypt seem to be built.
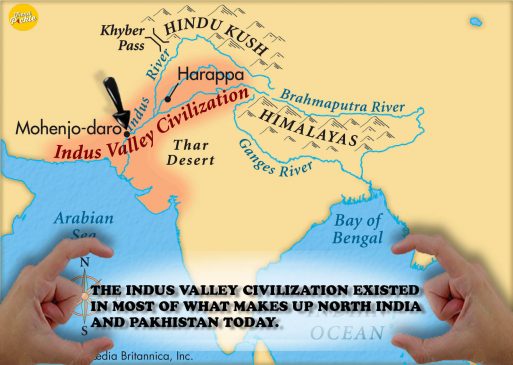
2. The Indus Valley civilization existed in most of what makes up North India and Pakistan today. It extended to the Iranian border, Gujarat, and Bactria.
3. The whole city of Mohenjo-Daro was spanned across 500 acres which is very large as per that time. The 5,000-year-old city could host a population of 40,000.
Have you heard about Grand canyon of India? Here is the complete guide to Gandikota fort – Grand canyon of India
4. The city of Mohenjo-Daro was divided into two districts, The Citadel, and Lower Town. The City’s exception monuments were present in The Citadel district.
5. Buildings in Mohenjo-Daro were made of fired and mortared bricks, as well as some sun-dried mud bricks and some wooden structures.
6. 900 Square feet Great bath (water tank) built with walls of bricks was built in Citadel district which worked as a public pool. it was 8 feet deep, 23 feet wide and 39 feet long. many small changing rooms were found around the bathing pool. even changing rooms had attached bathrooms. Seems like they were conscious about hygiene too. They knew it’s necessary to take a bath before and after using a public bath.
7. It is also fascinating that multistoried buildings were found at the site of Harappa and Mohenjo Daro.
8. There are around 1,500 sites of the Indus Valley Civilization and no sign of warfare or weapons have been found. This implies that the Indus natives were peaceful in nature, which might have made it vulnerable to foreign invaders.
9. The mode of transport during the Indus Valley Civilization may be bullock carts and white horses. Archaeologists found a clay bullock cart in the city of Mohenjo Daro, which indicated that bullock carts were used as a mode of transport.
10. Mohenjo-Daro had a marketplace in its central region.
11. The city also had a sophisticated water system. Houses had toilets and baths with proper water sewage system. This suggests that residents had an impeccable sense of urban planning. The city also had very advance waste disposal management system and all drains were covered.